Understanding the Differences Between a Proxy vs. VPN?
What are the primary differences between a proxy vs. VPN? Consumers and organizations around the globe are becoming more and more careful about what they share online and how. Data privacy is a top concern, since hackers are continuously updating their strategies and getting better at finding workarounds to security tactics.
Marketers are also finding new ways to create more personalized experiences, requiring more data about online behavior. One report found that 69% of consumers are concerned about how their personal information is collected on their devices, and 75% of people think they have reason to be worried about their data being used without their permission.
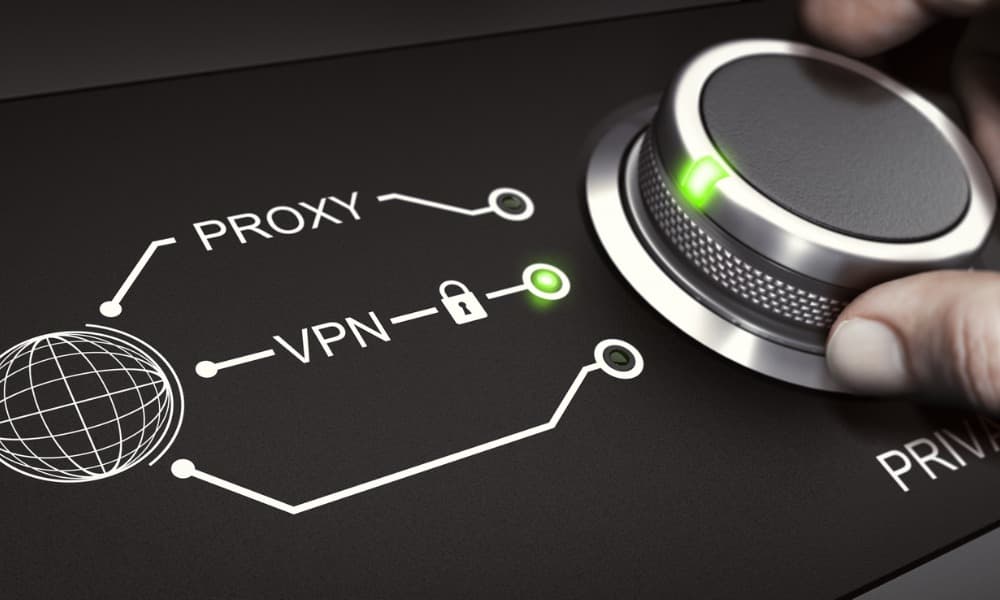
People often refer to virtual private networks (VPNs) and proxy servers interchangeably. Both of these cybersecurity tools hide user identities and allow you to access geo-restricted content from anywhere, but there are significant differences between VPNs and proxy servers.
Many organizations and individuals decide to use a VPN or a proxy so that their activity isn’t linked back to them. They also do it to access content that is blocked because of where their device is located (known as geo-blocking). Both of these options will do the trick, but a VPN takes things a step further and could be the right option if you are more concerned with overall data privacy.
This guide defines VPNs and proxy servers, looks at the differences between proxy vs. VPN, and explains when each option would work best in your specific situations. We’ll try to point you in the right direction for either personal or business use.

2 Great Reasons to Use a VPN or Proxy
VPNs and proxies are similar in that they both allow your computer to connect to another server, and your IP address is hidden. Why would you want to do this? Here are a few reasons why you would need a proxy vs. VPN:
1. You Want To Browse Anonymously & Protect Your Data
Sometimes you may not want your IP address to be tracked when you visit a website or are conducting activities online. Both VPNs and proxies can help you browse the web anonymously. The sites you’re visiting cannot see your IP address, and they will not restrict content based on your address. They only see the IP address of the proxy or VPN server.
Encryption techniques ensure that your sensitive information isn’t visible to online hackers or bad actors. You need a solution so no one can view the actual data being transmitted.
Both VPNs and proxies allow you to get on the internet anonymously, whatever your reason may be. These methods have their pros and cons, but a VPN is generally the more secure option when your focus is privacy protection.

2. You Want To Access Restricted Content
VPNs or proxies allow you to bypass a restriction if you’re trying to do something and you see an error message. A popular use for VPNs and proxies is to view geo-blocked content. Say you’re traveling to another country for work, but you want to use a video streaming service that only works in your home country. You can use a VPN or a proxy to make it look like you’re in your home country. You can also use both options from home to make it look like you’re in another country, so you can access content restricted to that country. You can choose from various countries and even cities when setting up your VPN or proxy.


Proxy vs. VPN at a Glance
A VPN is a virtual private network that encrypts any data you send or receive while you’re online and masks your IP address. Any third parties trying to monitor your activity won’t be able to see what you’re doing.
A proxy server is a computer that acts as a gateway between you and another server when you’re online. You would typically connect directly to a website and download the pages, but a proxy gets all of that information first and then passes it over to you.
You first connect to this proxy server, or outside host server, and then conduct your activities so no one can see your identity or IP address. Any third party will only see the proxy’s IP address and not yours. The three types of proxies are HTTP, SOCKS, and transparent.
Both VPNs and proxies hide your IP address and location to protect you from hackers. Your internet activity is kept private with both of these methods, whether you’re sending emails, streaming videos, or downloading or uploading files.
Overview of Proxy Servers
A proxy server is essentially a go-between for your device and the websites you’re visiting. The website you’re on cannot see your IP address — instead, it sees the IP address of the proxy server. Opening an incognito window on your browser is an example of using a proxy server.
Here’s an example: Say someone is over their limit for free articles from a news website. The website uses the user’s IP address to identify them and track their visits. The site won’t know who they are, however, if they use a proxy server to access the site.
Overview of VPNs
A VPN, like a proxy server, also hides your IP address so the websites you’re visiting cannot see your location or other details. It goes a step further, however, and encrypts all the traffic between your device and the internet.

4 Primary Differences Between a Proxy vs. VPN
Which of these options you choose depends on your objectives. Those most interested in protection from hackers will have different needs from those just wanting to guard their privacy. Take a look at how VPNs and proxies differ for the following web activities. Their ability to hide your IP addresses to protect your identity or access restricted content are not the only elements you need to consider when deciding if you should use a proxy or a VPN. There are many important differences when you’re deciding between each of these methods. Here are five primary ways they differ:
1. Privacy Levels
VPNs work on an operational level. Installing a VPN on your device causes it to encrypt all your internet traffic. The encryption applies whether you’re accessing the internet through an app or a browser. You can easily find a VPN provider with a no-log policy, which means they will not record your activity for the purpose of selling that information to another party.
Proxy servers, especially free ones, could sell traffic data to someone else. A proxy server only affects traffic that you access through the proxy application. Setting up a proxy server on your browser, for example, affects the traffic going through your browser. The proxy will not come into play if you open an app that connects to the internet but doesn’t use your browser.
A proxy hides your IP address from the website you’re visiting or a specific app you’re using, while a VPN does that while also redirecting all traffic within the operating system, including activity on your browser and any applications.

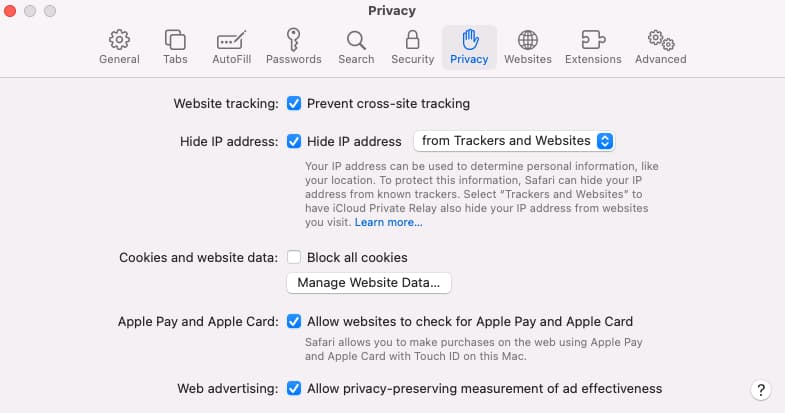
A Note on Web Browsers
Apple has been impressive recently in its quest for privacy. So, if you have the option to use a Safari browser, you can see by this image how Safari has an almost built-in browser proxy.
A Note on Preventing Tracking From Your ISP
A VPN can prevent your ISP from tracking your actions. Your ISP can generally see everything you do on their network, and they can track every site you visit. Using a VPN ensures that they cannot see anything. A proxy, in contrast, cannot prevent ISP tracking.
A proxy is a great choice for occasional use if you want to block your IP address or access geo-restricted content once in a while. A VPN, on the other hand, is the best option if you want to enhance your cybersecurity and prevent ISPs and others from tracking your online activity. Choosing a VPN, along with a digital file shredder, is a good step toward better security.

A Note on Protecting Yourself From Hackers
A proxy cannot protect you from hackers because it does not encrypt your data. A VPN, in contrast, encrypts all your data so hackers cannot see what information you’re transmitting.
2. Traffic Encryption
VPNs encrypt all traffic and data, so hackers cannot get their hands on the information passed between you and the VPN server. Say you jump on public Wi-Fi at the local coffee shop, and a hacker is on the same network trying to steal information from users. They won’t be able to see what you’re doing because all your traffic is encrypted. VPNs thus protect your sensitive data more than a proxy does.
Many proxy servers encrypt traffic, but not all of them. The proxy prevents the websites you visit from seeing your IP address, but a hacker on the coffee shop Wi-Fi mentioned above may be able to see the traffic going from your computer to the internet.

3. Cost
VPNs tend to cost more, and some proxy servers are easy to obtain for free. Most browsers have proxy tools that you can use without buying anything. VPNs can be free, but for the best quality service, you should expect to pay. They don’t provide that extra layer of security, however, but they are more affordable if you simply need to protect your IP address.
Most VPN providers charge a monthly subscription fee that varies based on the services provided and the traffic handled. Buying a VPN for personal use, for example, is a lot cheaper than installing one on your business network.
The bottom line is that a proxy is best for anonymous web browsing and accessing geo-restricted content. A VPN can serve that same purpose, as well as protecting your information from hackers and further protecting your privacy. The right option will depend on your intended activities as well as your budget.

4. Connection Speed
VPNs tend to be slower than proxies because they have to encrypt all their traffic, but the tradeoff is getting a greater level of security than a proxy server can offer. You may come to find that both VPNs and proxies can slow down your connection. Free proxy servers are usually slower since VPNs have more robust configuration settings. Make sure you understand these key differences when you’re deciding between a proxy vs. VPN.

Sometimes you need sensitive information erased from your device permanently. Maybe you’re organizing your files and getting rid of duplicates, or you are selling your computer and need everything wiped. There are many cases where you must be sure that files are gone for good.
Shred Cube can help you improve your digital security regardless of your choice between a proxy vs. VPN. Shred Cube plugs into your USB drive and allows you to permanently shred digital files so they are unrecoverable. The usual deletion process doesn’t shred your files — it keeps them on the hard drive, where hackers can still get to them.
Shred Cube gives you the ability to permanently delete files, including financial, corporate, personal, or legal documents you no longer need on your devices. You never want your sensitive information to get into the wrong hands. We make sure it is completely unrecoverable.
The USB plugin is safer than digital file shredders that require a download, because malicious code can infiltrate your computer even from seemingly secure downloads. Shred Cube is the first and only USB file shredder. Simply drag-and-drop your files to delete them or locate all your duplicate files for better organization. Our product was built to protect your privacy.
-
Data Destruction
The Shred Cube
Rated 2.81 out of 5$79.95Original price was: $79.95.$59.95Current price is: $59.95.